PROPOSED PAYMENT PROCESS
PRESENTATION PLAN
- Broad Features
- Tax Types & Modes of Payment
- Stakeholders
- Basic Features
- Workflow for Payment under various Modes
- Features of Accounting Process
- Proposed Accounting system
- Banking arrangements
- Reconciliation of receipts
- Redressal of grievances
BROAD FEATURES
- Electronic payment process- no generation of paper at any stage
- Single point interface for challan generation- GSTN
- Ease of payment three modes including CC/DC & NEFT/RTGS
- Common challan form with auto-population features
- Use of single challan and single payment instrument
- Common set of authorized banks
- Payment through any bank
- Common Accounting Codes
TAX TYPES & MODES OF PAYMENT
- Under GST, 4 types of Taxes to be paid- CGST, IGST, Additional Tax and SGST
- Three Modes of Payment
- Electronic including CC/DC (Mode I)
- Over The Counter Payment (for Payments upto ₹ 10,000/-) (Mode II)
- Payment through RTGS/NEFT (Mode III)
- Payment can be accepted by Departmental officers in enforcement cases only
STAKEHOLDERS
- Taxpayer
- GSTN (Goods and Service Tax Network)
- Authorized banks
- one e- FPB (Electronic Focal Point Branch) for each bank (in Mode I & II) to maintain government account and report all receipts
- all branches for receiving Over the Counter Payments
- one or more front end service branch
…. STAKEHOLDERS
- All Banks- for NEFT/RTGS Mode of payment
- Reserve Bank of India
- e- FPB (in Mode III)
- Aggregator for accountal & reconciliation of receipts
- Accounting Authorities of Centre & States
- Tax Authorities of Centre & States
BASIC FEATURES….
- Electronically generated Challan from GSTN for all 3 modes containing a unique 14-digit Common Portal Identification Number (CPIN) for each challan
- Challan can be generated by
- Taxpayer
- His authorized representative
- Departmental officers
- Any other person paying on behalf of taxpayer
- Certain key details like name, address, email, GSTIN of payer to be auto-populated
- Single challan / instrument for payment of all four types of taxes
- Challan once generated to be valid for 7 days
- Time of payment: from 0000 hrs. to 2000 hrs.
- Proposed workflow of RBI’s e-Kuber model to be followed for payment, accounting and reconciliation:
- Accounting Authorities to interact directly with RBI & not with Authorized banks in case of discrepancies found during reconciliation
- System of electronic Personal Ledger Account (cash ledger) on GSTN for each taxpayer (20 pages)
- One e-FPB per Authorized Bank (in Mode I & II) / RBI (in Mode -III)
- GSTN to be anchor in payment process with responsibility for information flow to various agencies
- RBI to act as aggregator and anchor of flow of fund and information about receipts
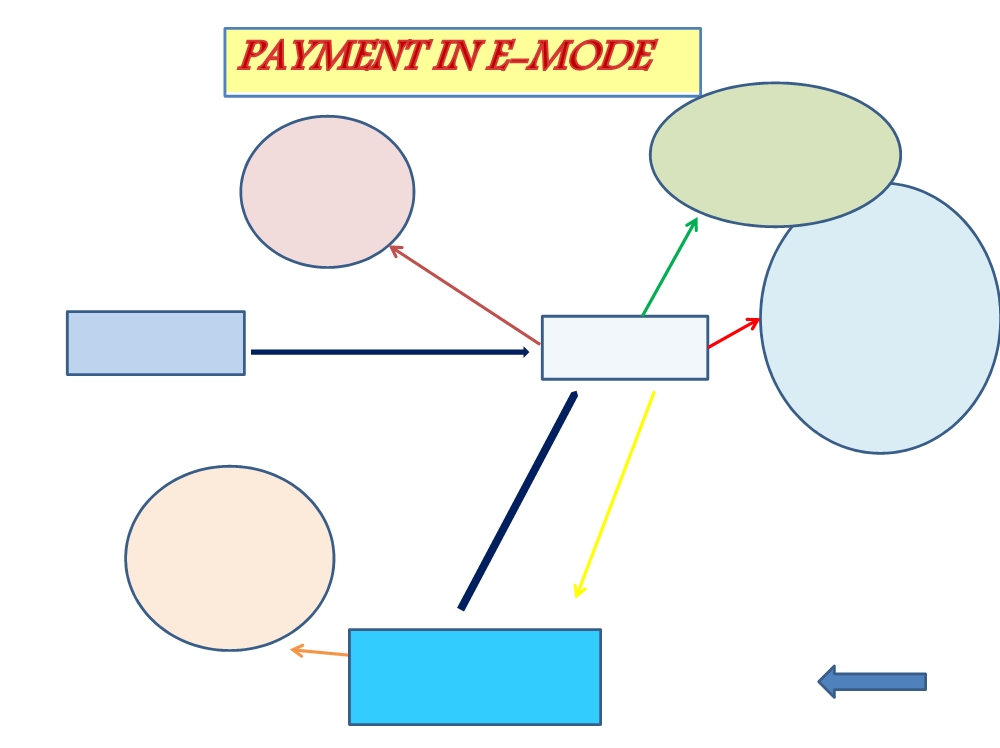
WORK FLOW FOR PAYMENT UNDER MODE -I ….
E-payment mode through authorized banks (internet banking , CC/DC):
- Generation of e-Challan at GSTN
- Tax payer to select e-payment mode
- Net Banking
- Credit/Debit Card of any bank
- Tax Payer to choose Authorized bank in case of Net Banking
- Payment gateway of authorized bank (or their SPVs) in case of CC/DC
- Credit Card proposed to be used by taxpayer to be registered at GSTN - as an additional safety check to eliminate the issue of charge back
- GSTN to direct the taxpayer to the website of selected bank/payment gateway
- Alongside, GSTN to forward an electronic string to the selected bank carrying specified details of challan on real time basis
- Taxpayer to make payment using the USER ID & Password provided by his bank
- On successful completion of transaction, e-FPB of bank to forward a confirmation electronic string (CIN) to GSTN on real time basis
- GSTN to credit the Taxpayer’s ledger
- Copy of paid Challan to be available on GSTN for taxpayer (downloadable/printable)
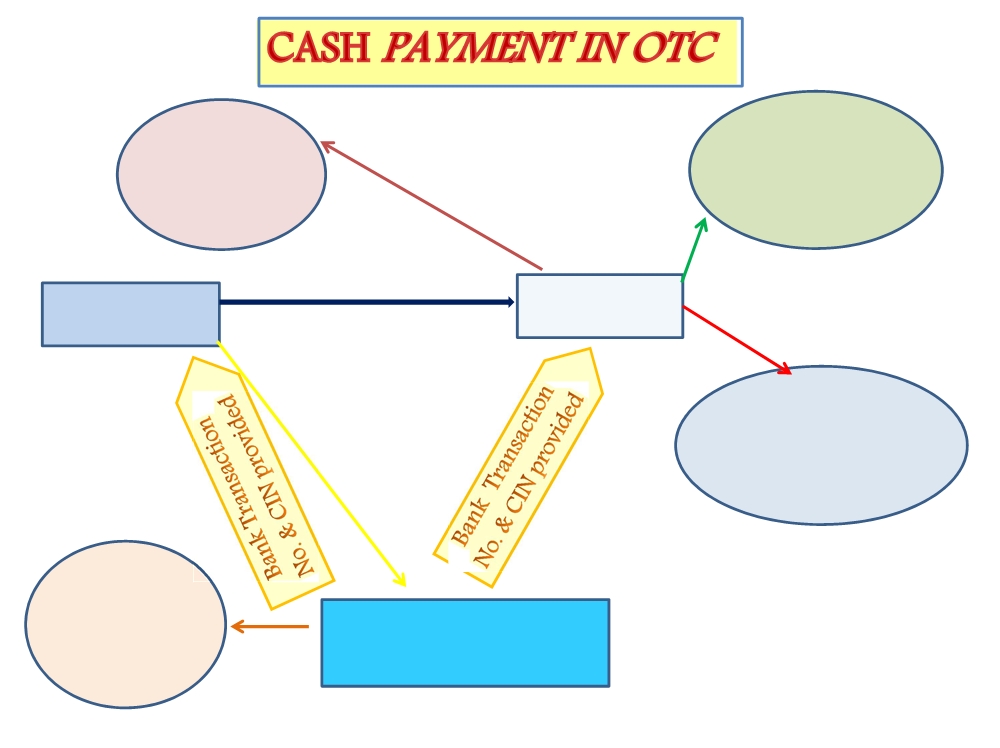
WORK FLOW FOR PAYMENT UNDER MODE -II ….
Over the Counter Payment:
- For small taxpayers for making payment upto ₹ 10,000/- per challan - by cash / DD / cheque drawn on same bank or on another bank in the same city
- Tax payer to tender only one instrument to pay one or more type of tax
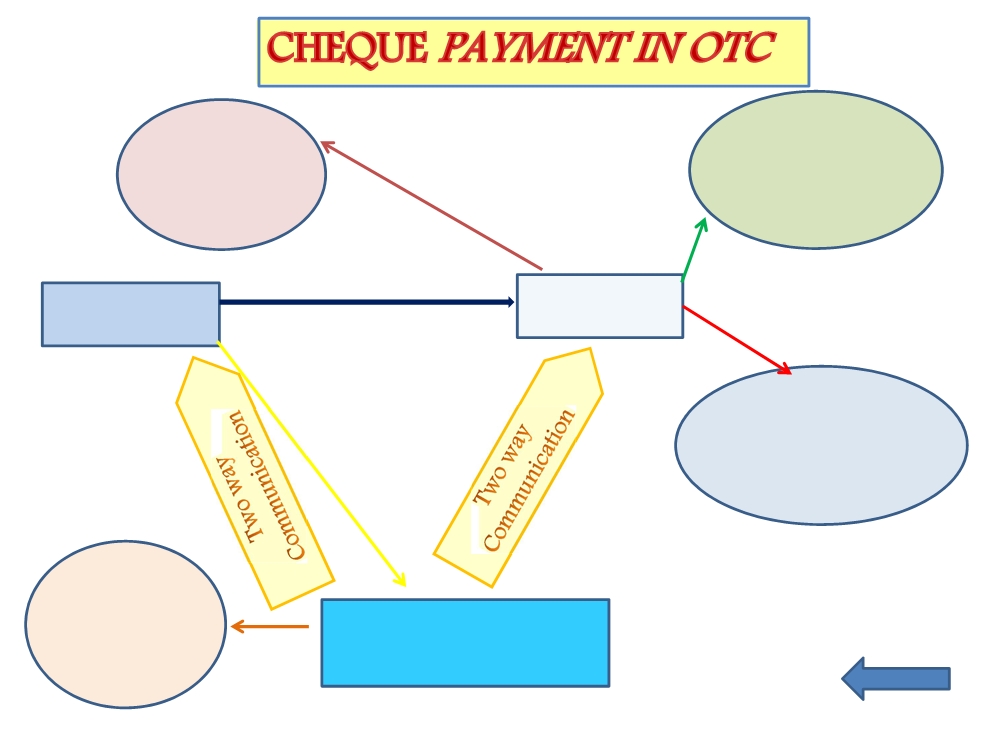
- For cheque payment, name of authorized bank & its location to be mandatorily filled in challan
- On real time basis, GSTN to share challan details with Core Banking System (CBS) of the selected authorized Bank
- Taxpayer to approach the branch of the authorized bank for payment of taxes along with the instrument or cash
- In case of cash / same bank instrument a unique transaction number (BTR/BRN) will be generated immediately by the authorized bank’s system and given to taxpayer
- Authorized bank to send receipt information (CIN) to GSTN on real time basis
- In case of instruments drawn on another bank in the same city, payment would not be realized immediately
- Authorized Bank to inform GSTN on real time basis in two stages
- when an instrument is given OTC - to send an electronic string to GSTN containing specified details
- second acknowledgement - after the cheque is realized with 3 additional details
- Similarly, bank to issue acknowledgement to taxpayer in two steps
- Acknowledgment of cheque immediately
- Upon realization of cheque, issuance of BTR / BTN
- GSTN to credit the Taxpayer’s Ledger
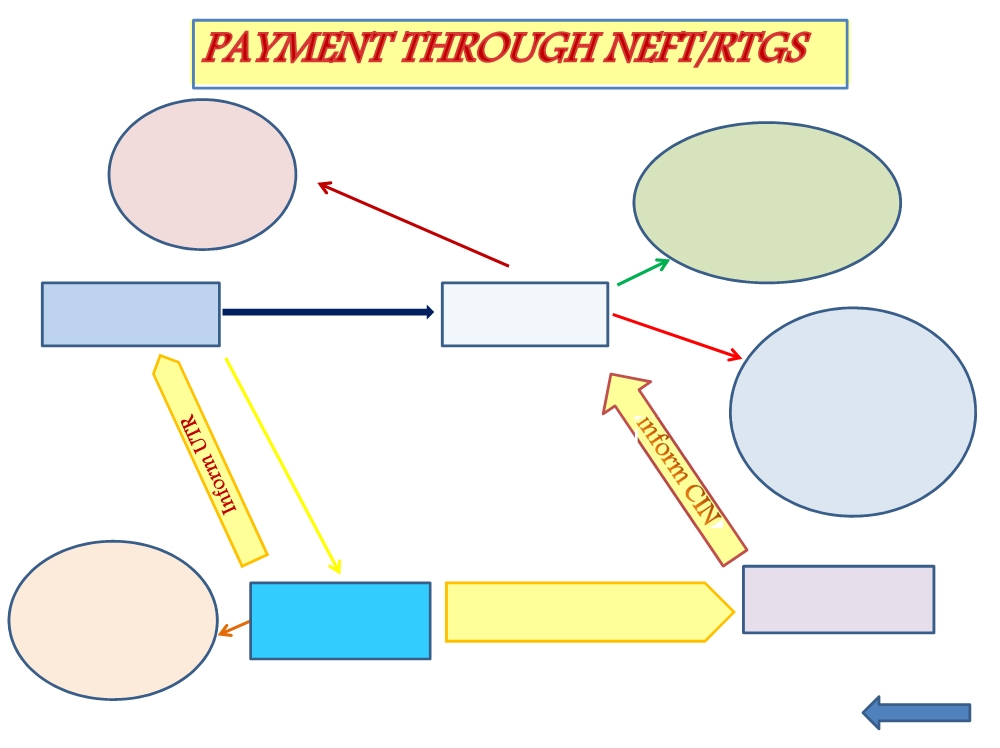
WORK FLOW FOR PAYMENT UNDER MODE -III….
Payment through NEFT/RTGS from any bank
- To be made operational after a pilot run by RBI
- For taxpayers:
- not having a bank account in any of the Authorized Banks
- having a bank account in any of the Authorized Banks
- No limit on amount to be paid through this mode
- Payments to be collected by RBI directly
- RBI to perform the role of e-FPB also
- Challan and NEFT/RTGS mandate form generated on GSTN
- NEFT/RTGS mandate form to have validity period of CPIN printed on it
- In challan, the field for name of Authorized Bank to be auto-populated as RBI
- NEFT/RTGS mandate form will have certain information auto-populated:
- CPIN in “Account Name” field
- ‘GST Payment’ in “Sender to Receiver Information” field
- Taxpayer to print a copy of Challan and NEFT/RTGS mandate form from GSTN & approach his bank for payment
- Amount indicated for remittance to be transferred by bank to the designated account of the government in RBI along with challan details and a Unique Transaction Reference (UTR) Number
- RBI to validate payments against each challan with UTR received from remitter bank
- RBI to report receipt of payment to GSTN (CIN) on real time basis through an electronic string with specified details
- GSTN to credit the Taxpayer’s ledger
FEATURES OF ACCOUNTING PROCESS….
- Authorized Banks to send list of CIN-wise details (electronic luggage file) for each type of Tax (CGST, IGST, AT & SGST) per day to RBI and Accounting Authorities at End of Day (EOD)
- RBI through its e-kuber system to consolidate the lists received from all authorized banks, debit their accounts and correspondingly credit Tax accounts of GOI / respective State Governments
- RBI to send digitally signed one e-scroll for each type of Tax (CGST, IGST, AT & SGST) per day (39) to Accounting Authorities of Central Government and State Governments & GSTN on T+1 basis
- GSTN to send reconciled data (challan data from Authorized Banks and e-scroll from RBI) to Accounting Authorities at EOD
- For any discrepancy noticed, accounting authority to generate a Memorandum of Error (MOE) & send to RBI
- RBI to resolve the discrepancy in consultation with the Authorized Bank
- RBI to report the corrected data to respective Accounting Authority & GSTN
- Taxpayers Master data to be provided by Tax Authorities to Accounting Authorities for mapping of payment details jurisdiction wise
PROPOSED ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
- Four different Major Heads of accounts to be opened for each tax along with underlying Minor Heads to account for various taxes & other receipts like interest, penalty, fees & others
- Standardized uniform Accounting Codes for all taxes under GST regime among Centre, State & UTs to facilitate settlement of IGST on the basis of centralized reporting
- Common Accounting Codes for Centre & States
BANKING ARRANGEMENTS
- Common set of Authorized Banks comprising existing authorized banks of the Central Government & all State Governments/UTs (presently 26)
- Certain minimum standards to be met by banks to become authorized banks
- A system of penalty/incentive proposed for reporting of error free data
- Payments through non-authorized banks permitted (NEFT/RTGS)
RECONCILIATION OF RECEIPTS
- Use of only system generated challans - no re-digitization by any actor in the entire work flow
- CPIN to be generated by GSTN -- to be used as a key identifier up till receipt of payment by Bank
- CIN (actual indicator of receipt of payment) to be generated by collecting Bank -- to be used as a key identifier thereafter for accounting, reconciliation, etc.
- Accounting Authorities to play a paramount role in reconciliation -
- Accounting on the basis of RBI data
- Reconciliation on the basis of GSTN and bank data
GRIEVANCE REDRESSAL
- In OTC mode if cash ledger of taxpayer not credited within three days- approach bank where instrument presented
- In RTGS/NEFT mode if cash ledger of taxpayer not credited within three days- approach bank where taxpayer’s account is
- Each e-FPB required to have front end service branch to resolve payment related issues