The Department of Financial Services (DFS) continued the momentum of reforms, building on the foundation laid by earlier initiatives like the EASE Reform agenda — focusing on risk assessment, NPA management, financial inclusion, customer service, digital transformation, and more.
The EASE Reforms, governed by the EASE Steering Committee of the Indian Bank's Association, have become deeply ingrained in all PSBs. The journey, spanning from EASE 1.0 to the current EASE 6.0, has witnessed a transformative shift, emphasizing digital customer experience, analytics-driven business improvement, tech and data-enabled capability building, and HR operations enhancement. The EASE Awards event recognizes banks for their outstanding performance in implementing the reform agenda.
Notably, the DFS's strategic intervention has played a crucial role in the significant reduction of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) in Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs). Gross NPAs have decreased from Rs. 9,33,779 crores in March 2019 to Rs. 5,71,515 crores in March 2023, demonstrating the effectiveness of measures such as the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), amendments to the SARFAESI Act, and the Prudential Framework for Resolution of Stressed Assets.
In the realm of digital payments, the DFS has been at the forefront of promoting a robust ecosystem. The DIGIDHAN Mission, now under the DFS, has played a pivotal role in the phenomenal growth of digital payment transactions in India. The total number of transactions has surged from 2,071 crores in FY 2017-18 to an impressive 13,462 crores in FY 2022-23. BHIM-UPI, a major driver in this growth, recorded over 1,000 crore transactions in a single month in August 2023.
Financial inclusion remains a key focus area, with initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana, MUDRA, Stand Up India, and Atal Pension Yojana making significant strides. The DFS's efforts have ensured that millions of citizens, especially those in vulnerable sections, have access to basic banking services, insurance, and pension schemes.
In the agriculture sector, the DFS has facilitated the robust disbursement of credit, with the Agricultural Credit increasing from Rs. 8.45 lakh crore in FY 2014-15 to Rs. 21.55 lakh crore in FY 2022-23. The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme has played a pivotal role in providing timely and hassle-free credit to farmers, with over 7.36 crore operative KCC accounts.
Overall, the Department of Financial Services has been instrumental in shaping a resilient and progressive financial landscape in 2023, contributing to the economic growth and well-being of the nation.
Following are some of the major achievements of the Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance, in 2023:
Enhanced Access and Service Excellence (EASE) Reforms:
- Gyan Sangam, under guidance of the Prime Minister in March 2016 at Pune, was the trigger for initiating reforms in Public Sector Banks and later, under guidance of Department of Financial services (DFS), EASE Reform agenda was born out of recommendations made by PSB’s Whole Time Directors (WTDs) and Senior executives in the PSB Manthan event in November 2017.
- EASE was conceptualized to improve Risk assessment, NPA management, deepening financial inclusion, enhance Customer service, initiate Digital transformation, Retail and MSME Credit off-take, develop Analytical capabilities, HR transformation and Governance etc.
- EASE Reforms are governed by EASE Steering committee of Indian Bank`s Association. It aims to bring an exhaustive and all-inclusive revamping and enhancing the capabilities of PSBs to meet the changing demands of the banking landscape. It also offers a common platform for all mid-size and large banks to establish and reinforce industry`s best practices resulting in better services and improved experience for the customers of PSBs at large.
- It focuses on collaborative development for all PSBs through regular Knowledge series and best practice workshops conducted by Champion banks and Market experts. Reform objectives are publicly reported, independently measured, benchmarked and reviewed Quarterly by the Bank Boards, and has significant weight in performance appraisals of WTDs.
- EASE Reforms Agenda is now deeply ingrained in all PSBs. It has been a key priority for bank leadership since FY19. While first two versions of EASE focused on building a firm foundation addressing key operational and capability gaps. EASE 3.0 (FY21) and EASE 4.0 (FY22) focused on building new-age capabilities based on digital innovations and analytics insights, accelerating PSBs performance through data driven advanced technological initiatives.
- Banks are recognized for their performance in EASE Agenda in the EASE Awards event every year by the Hon’ble Finance Minister.
- After 4-years of successful EASE journey and with all 12 PSBs turning profitable, another brainstorming event, PSB Manthan 2.0, was held in April 2022 with entire leadership of PSBs under guidance of the Department of Financial Services to take EASE to next level. EASENext program was born as its outcome with a significantly bigger, bolder and broader scope having two Pillars:
- Pillar1- EASE Common Reform Agenda- continues to drive EASE reform initiatives in the same format.
- Pillar2- 3-Year Bank Specific Strategic roadmap- Banks set up their own Bank specific 3-year strategic roadmap to focus on transformation reforms beyond common EASE reform agenda.
- Under Pillar1, EASE 5.0 (FY23) focused on enhanced digital customer experience, with emphasis on technology integration including emerging cloud adoption, account aggregator, open APIs and data-driven, integrated and inclusive banking solutions.
- Present reform, EASE 6.0 (FY24) is conceptualized with 22 Action points under 4 Themes focused on:
- Delivering excellence in customer service with digital enablement: Hassle-free branch banking experience, Seamless call-center experience, intuitive mobile/internet banking, complaint redressal, customer acquisition, retention and relationship deepening and Inclusive near-home service delivery.
- Digital and analytics-driven business improvement: Comprehensive digital banking for MSMEs, Banking solutions for Agri value chain, Digital marketing for enhanced customer engagement, Digitally-enabled sourcing and servicing of CASA deposit base and Partnership banking.
- Tech and data enabled capability building: Strengthening specialized analytics function, Increased adoption of cloud technologies, Digital and analytics driven risk management, collections and recovery, strengthening cybersecurity and preventing cyber frauds.
- Developing people and enhancing HR operations: Analyze drivers for employee Productivity, promote gender diversity, Strengthening specialization, succession planning and leadership Development, Data-driven manpower planning, role clarity, and target setting.

Non-Performing Assets in Scheduled Commercial Banks
- Gross NPAs of SCBs have declined from Rs. 9,33,779 crores (gross NPA ratio of 9.07%) as on 31.3.2019 to Rs. 5,71,515 crores (gross NPA ratio of 3.87%) as on 31.3.2023. Further, the fresh slippage in respect of SCBs has declined from Rs. 3,01,795 crores (slippage ratio of 3.73%) during the financial year (FY) 2018-19 to Rs. 2,13,368 crores (slippage ratio of 1.78%) during the FY 2022-23. All the aforesaid information pertaining to FY 2022-23 are as per provisional data of RBI.
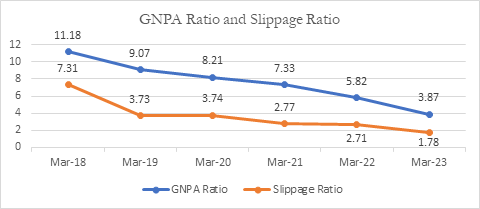
- Comprehensive measures have been taken by the Government and RBI to recover the bad debts, enabled by which, SCBs have recovered a total amount of Rs. 7.16 lakh crore (RBI provisional data for FY 2022-23) during the last five financial years. These measures include, inter alia, the following:
- Change in credit culture has been effected, with IBC fundamentally changing the creditor-borrower relationship. Up to June 2023, in case of CIRPs ending in approval of resolution plans, the realisable amount to the creditors was Rs. 2.92 lakh crore. The liquidation value of these corporate debtors was Rs. 1.74 lakh crore against the total admitted claims of Rs. 9.23 lakh crore.
- As on 13.9.2023, NARCL has made binding offers in 30 accounts with aggregate debt exposure of Rs 1,69,910 crores and out of these it has acquired/onboarded 4 accounts with exposure of Rs. 23,663 crores. Further, NARCL has been declared successful in swiss challenge in another 3 accounts having exposure of Rs 3,901 crores and Due diligence is underway in another 30 accounts having aggregate debt exposure of Rs 66,951 crores.
- The SARFAESI Act, 2002 has been amended to make it more effective. During the last five financial years, an amount of Rs. 1,51,428 crores have been recovered by SCBs through SARFAESI.
- Pecuniary jurisdiction of Debt Recovery Tribunal was increased from Rs. 10 lakh to Rs. 20 lakh. During the last five financial years, an amount of Rs. 72,708 crores have been recovered by SCBs through DRTs.
- Stressed Asset Management Verticals at PSBs have enabled stringent recovery, segregated pre- and post-sanction follow-up roles for clean and effective monitoring, and engaging specialised monitoring agencies for monitoring of large-value accounts. Through EASE Reforms Agenda, PSBs are being urged to improve recovery rate, role forward rate and role backward rate by adopting EWS system, various collection management and analytical tools.
- Prudential Framework for Resolution of Stressed Assets was issued by RBI in 2019 to provide a framework for early recognition, reporting and time bound resolution of stressed assets, with a build-in incentive to lenders for early adoption of a resolution plan.
- As a result of Government’s overarching policy response to recognition of stress, resolution of stressed accounts, recapitalisation and reforms in banks, the financial health and robustness of banking sector has since improved significantly:
- Asset quality has improved significantly with Net NPAs of SCBs declining to ₹1.36 lakh crore (0.95%) in Mar-23 from ₹2.04 lakh crore (1.67%) in Mar-22.
- Resilience has increased with Provision coverage ratio of SCBs increasing from 86.9% in Mar-22 to a healthy 90.9% in Mar-23.
- Enabled by implementation of comprehensive reforms, the financial health of PSBs has improved significantly, enhancing their ability to raise capital (in the form of both equity and bonds) from the market. PSBs have mobilised capital of ₹3,76,049 crore from the market from FY 2014-15 to FY2022-23.
Source: RBI provisional data for March 23 and PSBs

Digital Payments:
A. Progress of Digital Payments
- Promotion of digital payments ecosystem is an essential aspect of digital India programme and has the potential to transform Indian economy by extending inclusive financial services.
- Consequent upon the allocation of Business Rules vide the Cabinet Secretariat Notification No. 1/21/1/2017.Cab dated 15th February 2017; Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY) was assigned the responsibility of “Promotion of Digital Transactions including digital payments”. In compliance to the Union Budget announcement 2017-18, a dedicated DIGIDHAN Mission was set up at MeitY in June 2017. Promotion of Digital Payments has been transferred from MeitY to Department of Financial Services (DFS) vide Cabinet Notification No.1/21/6/2023-Cab. dated 17th July 2023.
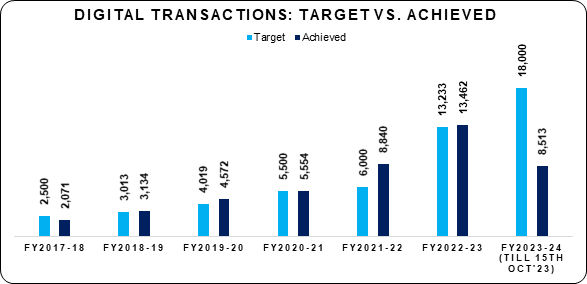
- The DIGIDHAN Mission has been the primary catalyst to promote the digital payment ecosystem in India. Digital payment transactions have registered tremendous growth in India over the last few years. The total number of transactions has increased from 2,071 crore in FY2017-18 to 13,462 crore in FY 2022-23. During the current financial year, i.e., FY 2023-24, 8,513 crore digital payment transactions have already been achieved, till 15.10.2023.
Figures in crores
Source: RBI, Digidhan Portal/Banks
|
- Citizens of the country have access to numerous easy and convenient digital payment modes such as BHIM-UPI, debit/credit cards, IMPS, NEFT, RTGS, AePS, NETC, PPIs which have registered substantial growth, transforming the digital payment ecosystem increasing person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) payments.
BHIM-UPI Achievement over the past 3 years
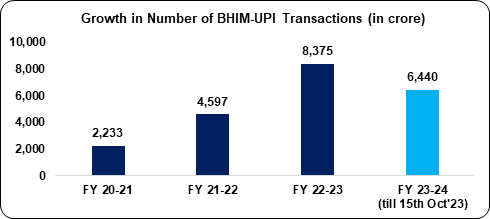
- BHIM-UPI transactions have grown significantly over the past three (03) years from 2,233 crore transactions in FY 2020-21 to 8,375 crore in FY 2022-23 at a CAGR of ~94%.
- BHIM-UPI has been the major driving force in the overall growth of digital payment transactions in the country accounting for 62% of digital payment transactions in FY 2022-23.
- In August 2023, BHIM-UPI reached another milestone recording over 1,000 crore (1,058.60 crore) transactions in a single month for the first time.
B Progression of UPI
- In a span of just over three years, from April 2020 to September 2023, the Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has experienced remarkable growth. With a surge from 1 billion transactions per month to a staggering 10 billion, UPI has redefined the digital payment landscape, setting new standards for innovation and user-centric features.
- In the year 2020, UPI introduced several groundbreaking features, each meticulously designed to cater to specific consumer needs. UPI AutoPay, for instance, caters to recurring payment needs, streamlining the experience for our customers. Furthermore, with the introduction of P2M Global transactions, Indian travellers now have the convenience of making UPI payments to foreign merchants, all through a single, familiar application. This advancement has revolutionized online payments for consumers and merchants alike.
- In the following year, 2021, UPI continued to innovate with the introduction of e-RUPI, 123Pay, UPI Plug-In, Aadhaar OTP onboarding, RuPay Credit Card on UPI, and UPI Lite. Each of these features has been meticulously designed to serve a range of customer needs.
- E-RUPI, for example, is a person- and purpose-specific voucher management system, presently allowing more than 13 government schemes to provide direct benefits to specific beneficiaries for designated purposes. To provide convenience of UPI to feature phone users, 123 Pay was introduced, currently available in 20 languages, thus reaching a broad demographic. Additionally, UPI now supports RuPay credit card transactions, enhancing the versatility of our platform. To augment efficiency and customer convenience, UPI Plug-In was introduced, seamlessly integrating UPI into various merchant applications, ensuring a native and user-friendly experience.
- To promote financial inclusion, Credit Line on UPI, Conversational Payments (Hello! UPI & BillPay Connect) and UPI LITE X were launched in September 2023.
- ‘Credit Line on UPI’ enables pre-sanctioned credit lines from banks via UPI and will revolutionize customer access to credit, fostering a more streamlined and digital banking ecosystem. With this, the process of availing, connecting, and utilizing credit lines will be significantly expedited, driving economic growth and progress.
- Conversational UPI Payments and Conversational Bill Payments underscores the emergence of AI-enabled transactions which will further deepen the reach and use of digital payments in the country. ‘Hello! UPI’, an AI-voice-enabled payment feature built by Bhashini (under MeitY) along with NPCI, allows users to make conversation-based UPI transactions in Hindi and English, using both feature phones and smartphones. This expansion will broaden payment accessibility for most Indians who are fluent in their native languages, providing significant benefits to senior citizens and the digitally inexperienced. Additionally, through ‘BillPay Connect’, customers can conveniently fetch and pay their bills by sending a simple ‘Hi’ on the messaging app or through their smart home devices by giving voice commands.
- 'UPI LITE X' addresses challenges of remote areas by enabling offline UPI payments and making digital transactions accessible even in low-connectivity regions. It will be accessible to anyone with a compatible device that supports Near Field Communication (NFC). In addition to Scan and Pay (QR), UPI NFC enabled phones can now be used to ‘Tap & Pay’. With this functionality, users now have the option to simply tap NFC-enabled QR codes at merchant locations to complete their payments.

Financial Inclusion Intervention:
a. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) was launched as the National Mission for Financial Inclusion on 28.8.2014. It aimed to ensure comprehensive financial inclusion of all households in the country by providing universal access to banking facilities with at least one basic bank account to every household, financial literacy, and social security cover.
The scheme offered:
- To unbanked persons a basic bank account without any minimum balance requirement, called a Basic Savings Bank Deposit (BSBD) account
- Free RuPay debit card, with in-built accident insurance cover of Rs. 2lakh
- Access to overdraft facility of up to Rs. 10,000, subject to eligibility conditions
- Easy access to banking services in rural areas, through Bank Mitras
- Awareness about financial products through financial literacy programmes
Progress under PMJDY (as on 04.10.2023):
- No of PMJDY Accounts: 50.63 crore
- Deposit in accounts: Rs 2,05,190 crore
- No of Women beneficiaries: 28.10 crore (55.5%)
- No of beneficiaries in Rural/Semi urban: 33.81 crore (66.8%)
- No of RuPay card issued: 34.36 crore

b. Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana
Salient Features:
- Rs.2 lakh term life insurance covers for death due to any reason.
- All Individuals Account holders aged between 18 to 50 years eligible to enrol.
- Annual premium Rs. 436/- per annum per member and on quarterly pro rata basis.
- Cover period: 1st June to 31st May.
- Renewable life covers for one-year period.
Achievements (As on 04.10.2023):
- Cumulative Enrolments – 18.19 Crore
- Cumulative No. of Claims Paid - 7,04,941
- Total Claim Amount Paid – Rs. 14,098.82 Crore

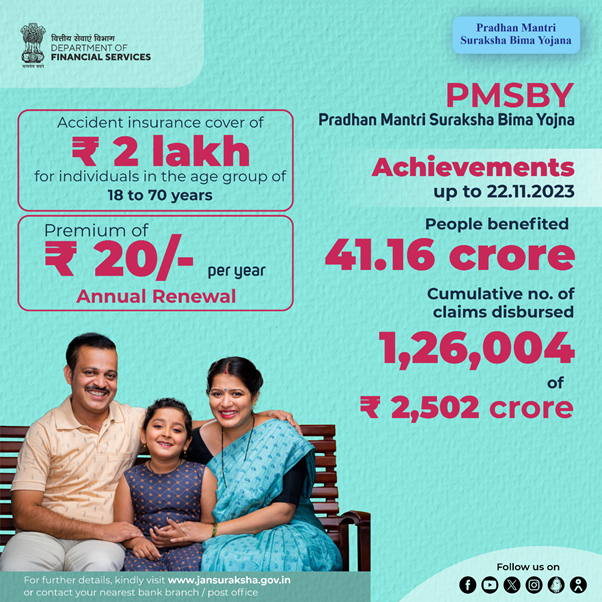
c. Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY)
Salient Features:
- Accidental insurance cover of Rs. 2 lakh payable on death / total disability and Rs. 1 Lakh on partial disability.
- All Individuals Account holders aged between 18 to 70 years eligible to enrol.
- Annual premium Rs. 20/- per annum per member.
- Cover period: 1st June to 31st May.
- Renewable life covers for one-year period.
Achievements (As on 04.10.2023):
- Cumulative Enrolments – 40.29 Crore
- Cumulative No. of Claims Paid –1,24,083
- Total Claim Amount Paid – Rs. 2,463.91 Crore
d. “MUDRA - Funding the Unfunded”
Features:
- Launched on 8th April 2015
- Purpose: For financing income-generating small business enterprises in manufacturing, trading and service sectors, including activities allied to agriculture such as poultry, dairy, beekeeping, etc. Term loan and Working Capital requirements can both be met
- Member Lending Institutions: Banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) & Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs)
- Categories: Shishu – upto Rs.50,000/-, Kishor – above Rs.50,000 & up to Rs.5.00 lakh, Tarun – above Rs.5.00 lakh & up to Rs.10.00 lakh
- No insistence on collateral
- Rate of Interest: Decided by lending institution, interest is charged only on the money held overnight by borrower
Status as on 06.10.2023:
- More than 43.74 crore loans amounting to Rs.25.51 lakh crore have been sanctioned since the launch of Scheme
- About 69% loans have been sanctioned to Women Entrepreneurs & 51% loans have been sanctioned to SC/ST/OBC category of borrowers
- Category-wise break-up:-
|
Category
|
Percentage as per No. of Loans
|
Percentage as per Amount Sanctioned
|
|
Shishu
|
82%
|
39%
|
|
Kishor
|
16%
|
37%
|
|
Tarun
|
2%
|
24%
|
|
Total
|
100%
|
100%
|
- Targets have been consistently met since inception of the Scheme, except for FY 2020-21 due to COVID-19 pandemic.

e. Stand Up India Scheme
Introduction:
- Launched on 5th April 2016
- Objective: To facilitate loans from Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) of value between Rs. 10 lakh and Rs.1 Crore to Scheduled Caste (SC) / Scheduled Tribe (ST) and woman borrower i.e. at least two loans per bank branch for setting up a greenfield enterprise. Greenfield enterprises in trading, manufacturing, services sectors & Activities allied to agriculture
- Scheme also envisages extending handholding support to the potential borrowers. It also provides for convergence with Central/State Government schemes.
Salient Features:
- Eligible borrowers: SC/ST/Women entrepreneurs above 18 years of age
- Composite Loan (inclusive of term loan and working capital) between Rs.10 lakh and Rs.100 lakh
- Loan for setting up a new enterprise in manufacturing, trading or service sectors and activities allied to agriculture.
Achievement:
- A total number of 47,073 (approx) SCs/STs and Women borrowers benefited under Stand- Up India Scheme as on 24.11.2023

f. Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
- Atal Pension Yojana (APY) is a flagship social security scheme of the Government of India, launched on 9th May 2015 by Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi with the objective of providing financial security during Old-age to all citizens of India, especially the poor, the underprivileged and the workers in the unorganised sector.
- Individuals between 18 to 40 years of age who have a savings bank account and who are not an income taxpayer can enrol under the scheme.
- The scheme provides a lifetime guaranteed pension to the subscriber ranging from Rs. 1000 to Rs. 5000 per month (as selected by the subscriber) from the age of 60 years.
- Guarantee of equal pension to the spouse after the death of the subscriber.
- In case of the death of both the subscriber and life partner (spouse), the nominee will receive the entire corpus accumulated till age 60 of the subscriber.
- Flexible contribution payment options- monthly, quarterly and half yearly have been made available.
- The amount of pension chosen and the individual’s age will decide the contribution amount till the age of 60 years.
Progress under APY during the last 8 years
- Atal Pension Yojana has been implemented comprehensively across the country covering all states and Union Territories with total gross enrolments crossing the mark of 5.97 crore. APY enrolments have continuously shown an increasing trend since its inception. As of date, the total assets under management (AUM) in APY is more than Rs. 31,290 crore and the scheme has generated an investment return of 8.88 % since inception of the scheme.
- This achievement of bringing in the most vulnerable sections of society under the coverage of pension has been made possible with the untiring efforts of Public and Private Banks, Regional Rural Banks, Payments Banks, Small Finance Banks, the Department of Posts, and the support extended by the State Level Bankers’ Committees. PFRDA keeps interacting with these banks to ensure the coverage of APY pan India basis and march owards pension saturation.
- The profile of the current subscribers shows that they are mostly young with 45 percent of them being in the age group of 18-25 years. The female participation under APY has shown significant growth and the total female enrolment has reached 46% of the total enrolment which is approx. 2.65 crore.
- For the benefit of subscribers and APY SPs, many initiatives have been taken on technical fronts which include the online/ digital module for enrolment (e-APY), the APY mobile app, podcasts on features & latest developments under APY. Keeping in view the importance of regional languages in canvassing the scheme, informative promotional materials such as APY flyers, radio jingles, 3-minute informative videos, etc. have been made available in Hindi, English, and other vernacular languages. Training on APY is now also conducted in regional languages besides Hindi and English.

Agriculture Credit & KCC:
- Ground Level Agricultural Credit (GLC)
- The Agricultural Credit disbursement has increased almost 2.5 times from Rs. 8.45 lakh crore in FY 2014-15 to Rs. 21.55 lakh crore in FY 2022-23.
- As a result of sustained and concerted efforts by the Government in the direction of providing access to concessional credit to the farmers the agri-credit has increased at an impressive average Annual Growth Rate of about 13% in the last 9 years.
- During 2022-23, the growth in agriculture credit has remained robust with disbursement level of Rs. 21.55 lakh crore against target of 18.50 lakh crore.
- A target of Rs. 1,26,000 crore was fixed for Animal Husbandry, Dairy, Poultry & Fisheries during the FY 2022-23. The total achievement in respect of allied activities was Rs. 2.62 lakh crore.
- Agriculture credit target for year 2023-24 has been set at Rs. 20.00 lakh crore with a sub-target of Rs. 2.93 lakh crore for Animal Husbandry, Dairying and Fisheries farmer.
Agriculture Credit Flow- Trends- 2014-15 to 2023-24
|
(In Rs. crore)
|
|
Year
|
Annual Target
|
Achievement
|
% Achievement
|
|
2014-15
|
8,00,000
|
8,45,328
|
106
|
|
2015-16
|
8,50,000
|
9,15,510
|
108
|
|
2016-17
|
9,00,000
|
10,65,756
|
118
|
|
2017-18
|
10,00,000
|
11,62,617
|
116
|
|
2018-19
|
11,00,000
|
12,56,830
|
114
|
|
2019-20
|
13,50,000
|
13,92,729
|
103
|
|
2020-21
|
15,00,000
|
15,75,398
|
105
|
|
2021-22
|
16,50,000
|
18,63,363
|
113
|
|
2022-23
|
18,50,000
|
21,55,163
|
116
|
|
2023-24
|
20,00,000
|
10,40,931*
|
52
|
* Data for FY 2023-24 as on 31 August 2023
- KCC Scheme
- Kisan Credit Card Scheme which had been in operation since August 1998, has emerged as an innovative credit delivery mechanism to meet production credit requirement of farmers in a timely and hassle-free manner. The KCC Scheme has since been simplified by providing the farmers with ATM enabled debit card based on one-time documentation, multiple withdrawals within the limit and built-in cost escalation in the limit, etc.
- KCC facility along with benefits of interest subvention extended to Animal Husbandry and Fisheries farmers for their Working Capital requirement up to Rs. 2.00 lakh within the overall limit of Rs. 3.00 lakh in February 2019.
- DFS has issued guidelines for issuance of KCC to Animal Husbandry and Fisheries farmers along with directions for timebound processing of duly acknowledged applications (within 15 days).
- The limit of collateral-free agricultural loan is Rs. 1.6 lakh. Further, in case of dairy farmers, the Milk Union can enter into a tie-up agreement with their members to avail collateral free loan above Rs. 1.6 lakh upto Rs. 3 lakh.
- Total number of operative KCC Accounts as on 30 June 2023 are 7.36 crores with total outstanding amount of Rs. 8.86 lakh crores. Of the 7.36 Crore accounts, 23.67 lakh accounts pertain to agri-allied sectors.
- Under Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS) of Department of Agriculture & Farmer’s Welfare provides interest subvention for short term crop loans of upto Rs.3 lakh @ 1.5% per annum to Banks on use of their own resources. Besides, the scheme provides additional interest subvention of 3% for prompt repayment of the loan, thereby reducing the effective rate of interest to 4%.
KCC Progress:
|
Year
|
Commercial Banks1
|
Cooperatives
|
RRB
|
Total
|
|
|
No. of Operative Accounts (in ‘000)
|
Amount
Outstanding in Operative
Accounts
(in Rs cr)
|
No. of
Operative
Accounts
(in ‘000)
|
Amount
Outstanding in Operative
Accounts
(in Rs cr)
|
No. of
Operative
Accounts
(in ‘000)
|
Amount Outstanding in Operative
Accounts
(in Rs cr)
|
No. of Operative Accounts
(in ‘000)
|
Amount Outstanding in Operative Accounts
(in Rs cr)
|
|
2018-19
|
23,632
|
4,55,079
|
30,414
|
1,27,436
|
12,253
|
1,27,072
|
66,300
|
7,09,587
|
|
2019-20
|
24,145
|
4,70,144
|
28,938
|
1,36,735
|
12,197
|
1,36,695
|
65,280
|
7,43,573
|
|
2020-21
|
30,696
|
4,56,736
|
30,183
|
1,46,981
|
12,891
|
1,49,416
|
73,770
|
7,53,133
|
|
2021-22
|
26,871
|
4,76,283
|
31,131
|
3,00,350
|
13,348
|
1,62,060
|
71,350
|
9,38,693
|
|
2022-23
|
28,296
|
5,18,636
|
31,344
|
1,89,235
|
13,829
|
1,77,604
|
73,469
|
8,85,475
|
|
2023-242
|
28,144
|
5,11,005
|
31,506
|
1,93,951
|
13,952
|
1,81,140
|
73,602
|
8,86,095
|
1 Commercial Banks excluding RRBs
2 Data for FY 2023-24 as on 30 June 2023

****
|
 9911796707
9911796707













