| News | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Driving Financial Empowerment |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-2-2025 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Transformative schemes boost financial inclusion, insurance, and entrepreneurship
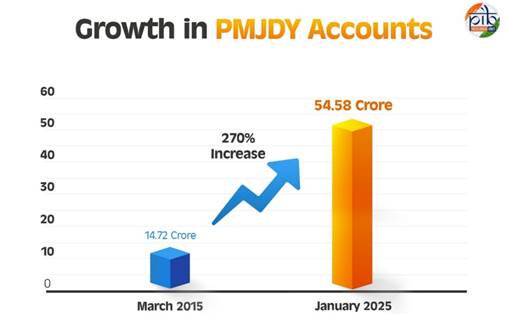
Synopsis Key government initiatives have significantly advanced financial inclusion and entrepreneurship, benefiting millions across India. The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) has opened over 54.58 crore accounts, with deposits rising to ₹2.46 lakh crore by January 2025. The Atal Pension Yojana (APY) has seen a surge in enrolments, reaching 7.33 crore by January 2025, with more than 89.95 lakh new enrolments in FY 2024-25. The Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) has enrolled 22.52 crore individuals, with ₹17,600 crore disbursed for 8.8 lakh claims. The Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) has covered 49.12 crore people, processing ₹2,994.75 crore against accident claims. The Stand-Up India Scheme has sanctioned ₹53,609 crore in loans for 2.36 lakh entrepreneurs, with a focus on SC/ST and women. Finally, the Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) has sanctioned ₹32.36 lakh crore for 51.41 crore loans, with 68% of the loans benefiting women and 50% going to SC/ST/OBC categories. These initiatives are instrumental in promoting financial empowerment and inclusive growth. Introduction Financial inclusion remains a key government priority, striving to provide banking, credit, and insurance services to the unbanked and underserved. Through initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, Atal Pension Yojana, and others, the government is working to empower individuals, secure financial futures, and promote entrepreneurship. The motto, "From Jan Dhan to Jan Suraksha," encapsulates the vision of financial security and inclusive growth for all. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) Launched in August 2014, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) aimed to bring the unbanked into the formal financial system by expanding access to savings accounts, credit, remittance, insurance, and pensions. Over the decade, it has empowered weaker sections and low-income groups, playing a key role in financial inclusion and economic integration. According to the World Bank's Global Findex Database 2021, bank account ownership in India more than doubled in the past decade, rising from 35 percent in 2011 to 78 percent in 2021.
Key Achievements:
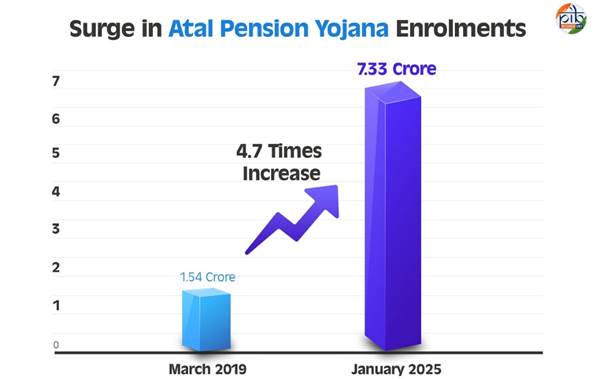
Atal Pension Yojana (APY) Launched on May 9, 2015, Atal Pension Yojana (APY) provides social security to unorganised sector workers. It ensures financial stability for the poor and underprivileged. The scheme was operationalised on June 1, 2015. APY is regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA). It functions under the National Pension System (NPS) framework.
Key Achievements:
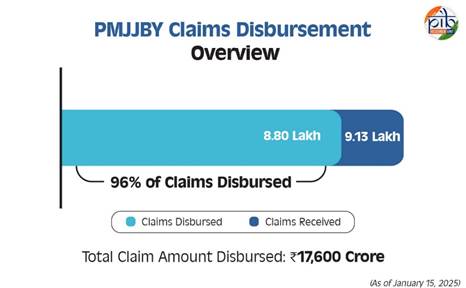
Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) Launched on May 9, 2015, Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY) is a government-backed life insurance scheme. Proposed in the 2015 budget, it aimed to expand insurance coverage beyond the then 20% of the population. The scheme provides one-year renewable life insurance covering death from any cause. Key Achievements:
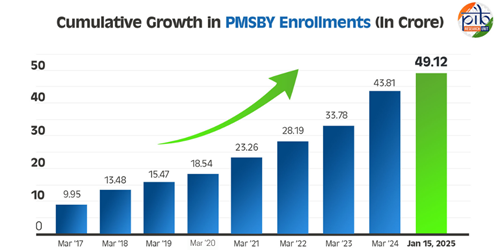
Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) Launched on May 9, 2015, Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY) is an accident insurance scheme covering death and disability. It is a one-year renewable policy aimed at increasing insurance penetration. The scheme provides coverage to individuals aged 18-70 with a savings or post office account, benefiting the poor and underprivileged.
Key Achievements:
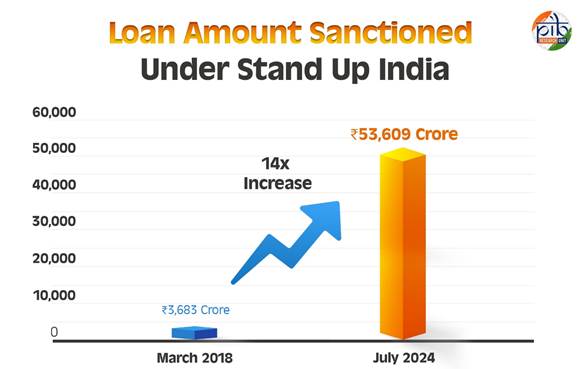
Stand-Up India Scheme Launched on April 5, 2016, the Stand-Up India Scheme promotes entrepreneurship among women, SCs, and STs. It provides bank loans from ₹10 lakh to ₹1 crore for greenfield enterprises in manufacturing, services, trading, and allied agriculture. The scheme aims to empower aspiring entrepreneurs by easing financial barriers.
Key Achievements:
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) Launched on April 8, 2015, Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) supports small and micro enterprises with loans up to ₹10 lakh. In Union Budget 2024-25, the loan limit was increased to ₹20 lakh. MUDRA facilitates financial inclusion by refinancing micro units and empowering aspiring entrepreneurs. Key Achievements:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 9911796707
9911796707