| News | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
HEALTH AN INTEGRAL COMPONENT OF SOCIAL WELFARE, LEITMOTIF FOR THE GOVERNMENT |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31-1-2023 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
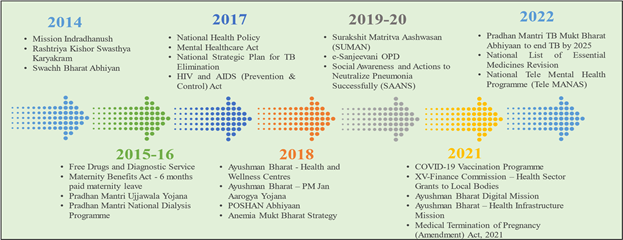
HEALTH AN INTEGRAL COMPONENT OF SOCIAL WELFARE, LEITMOTIF FOR THE GOVERNMENT COMPREHENSIVE AND ‘LEAVE NO ONE BEHIND’ APPROACH GUIDING PRINCIPLES OF HEALTHCARE Health is an integral component of social welfare, leitmotif for the Government. Comprehensive and ‘leave no one behind’ approach form the guiding principles of healthcare, as per the Economic Survey 2022-23 tabled today in Parliament by Smt Nirmala Sitharaman, Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs. Major initiatives from 2014 to 2022 for better overall health The pre-budget Survey notes that ensuring the provision of quality health facilities to citizens is an important priority for the Government. Towards this objective, multidimensional initiatives have been launched and carried forward for better overall health of the citizens, as encapsulated below. Under the National Health Mission, the Government has made concerted efforts to engage with all relevant sectors and stakeholders to move in the direction of achieving universal health coverage and delivering quality healthcare services to all at affordable cost.
Improvement in health-related Indicators The Economic Survey highlights that the Indian healthcare network is among the largest in the world. The results of an effective health approach are visible in the improvement in some of the important health-related indicators, as seen below.
Source: National Family Health Surveys (NFHS) 2015-16 and 2019-21, MoHFW With concerted efforts made under the Reproductive, Maternal, New-born, Child, Adolescent Health Plus Nutrition (RMNCAH+N) strategy, India has made considerable progress in improving the health status of both mothers and children. As per the Sample Registration System (SRS) data, India has successfully achieved the major milestone to bring the Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) to below 100 per lakh live births by 2020 (laid down in National Health Policy 2017) by bringing it down to 97 per lakh live births in 2018-20 from 130 per lakh live births in 2014-16. Eight states have already achieved the SDG target to reduce MMR to less than 70 per lakh live births by 2030. These include Kerala (19), Maharashtra (33), Telangana (43) Andhra Pradesh (45), Tamil Nadu (54), Jharkhand (56), Gujarat (57), and Karnataka (69). Following a steady downward trend, Infant Mortality Rate (IMR), Under Five Mortality Rate (U5MR) and Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR) have further declined as a result of countrywide efforts towards increasing health service coverage through strengthening of service delivery; quality assurance; RMNCAH+N; human resources, community processes; information and knowledge; drugs and diagnostics, and supply chain management, etc. Trends in Mortality indicators
Source: Sample Registration System |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 9911796707
9911796707